The Art of Nitrification
The introduction of nitro groups on top of the carbon atoms of organic molecules is a process known as nitrification. In the vast world of the chemical industry, nitrification reaction is known for its wide application and rapid development, especially in the field of large-scale manufacturing of explosives and energetic materials, scientists have made unremitting explorations on it, making the nitrification theory system increasingly perfect. The purpose of the introduction of nitro into aromatic rings and heterocycles mainly focuses on three levels: first, the conversion of nitro groups into other substituents, such as nitro reduction, which is one of the key paths for the synthesis of primary aryl amines; Secondly, the strong electrical absorption of the nitro group is used to activate other substitutive groups (especially chlorine groups) on the aromatic ring, which is convenient for the occurrence of nucleophilic substitution reactions. Finally, the unique properties of nitro are used to give fine chemical products specific properties, such as darkening the color of dyes, or as pharmaceuticals, explosives and mild oxidants.
Continuous evolution of nitrification process
The nitrification process is mainly divided into two types: batch type and continuous type. The batch nitrification process ensures that the nitrification reaction is carried out at a suitable temperature by adding mixed acids or raw materials to the reactor by droplets, and prevents the temperature from getting out of control due to excessive drip acceleration. However, due to the difference in the nature of the reaction, many unreacted raw materials will enter the separator after the end of the reaction and continue the reaction at high temperatures, triggering the reactor to heat up and increase the production risk. In contrast, the continuous nitrification process realizes the continuous feeding, reaction and separation through remote automatic control, avoids the repeated feeding and discharging process, ensures the accuracy of material ratio and the consistency of process indicators, greatly improves production efficiency, and reduces the labor intensity of workers. Although the country began to promote the continuous nitrification process during the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, the proportion of its industry application is still not high. Experts point out that one of the reasons why companies adhere to the batch nitrification process is the ability to flexibly adjust the process route according to market changes and produce more marketable products. At the same time, many chemical companies lack awareness of the dangers of the nitrification process and lack the motivation to upgrade. In the small-scale or pilot-scale stage of nitrification reaction, the risk is relatively low due to the small size of the reactor, the uniform material, and the easy control of the temperature. However, once industrialization scales up, so does the risk. Although the nitrification process is considered an exothermic reaction and has certain hazards, it should not be generalized and risk assessment should be carried out on a process-specific basis. Local governments, especially in major chemical provinces such as Shandong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu, have introduced a number of strict policies.For example, in early 2018. the Shandong Provincial Bureau of Work Safety issued the Notice on Conducting Safety Assessment of Explosive Chemical Production Equipment, which aims to conduct safety assessment of explosive chemical production equipment throughout the province. In the process of project selection, enterprises should choose intrinsically safe processes and prohibit the construction of unsafe processes. A blanket ban on the industry could lead to product shortages and price increases, which in turn would lead to illegal production by manufacturers who did not have safe production practices, causing greater harm.
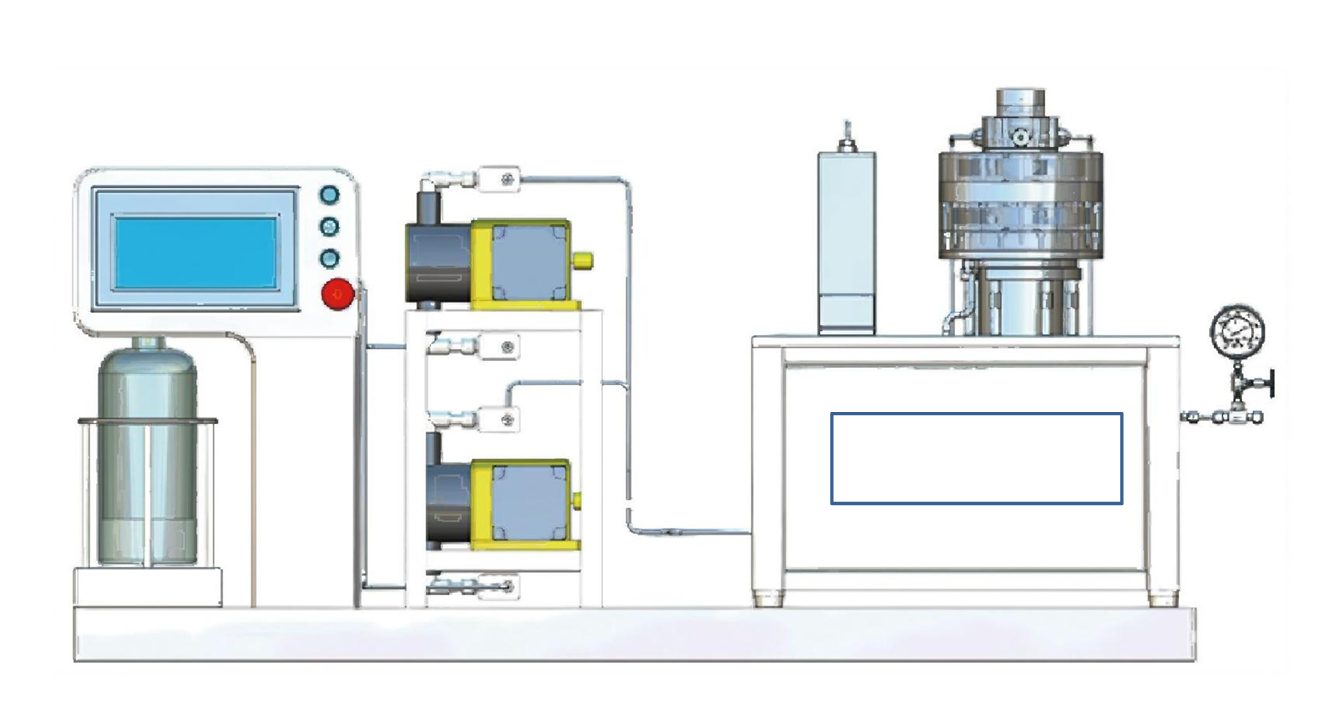
As a new type of environmentally friendly chemical technology, the micro-chemical technology represented by the microchannel reactor not only occupies a small area, but also has reasonable resource utilization and low energy consumption compared with the traditional chemical industry, and has received great attention from the fields of energy chemical industry and environmental engineering. The microchannel reactor uses precision processing technology to manufacture a continuous reactor with a characteristic size between tens of microns and a few millimeters, and its special channel structure significantly improves the mass transfer effect, providing an effective solution for the accurate, stable and safe nitrification reaction. The continuous flow microchannel reactor can be customized according to different processes, and the temperature, pressure, flow rate and other parameters in the reactor are precisely controlled, ensuring the safety and automation of the reaction system. The following examples illustrate the application of nitrification in microchannel reactors and the advantages compared to conventional processes:
(1) The nitrification reaction was carried out in a microchannel reactor using N-(l-ethylpropyl)-N-acetyl-3.4-dimethylaniline as raw material, and the results showed extremely high efficiency and safety.
(2) Using pyrazole as raw material, N-nitropyrazole is synthesized by nitrification of nitric acid-acetic anhydride system, and then 3.4-dinitropyrazole is synthesized by thermal rearrangement and further nitration, with efficient reaction process and high product purity.
(3) In the chlorobenzene nitrification experiment, the microchannel reactor performed well in improving the selectivity of the product, and the by-products were relatively few.
(4) The synthesis of 2.4-dinitrochlorobenzene is realized by a two-step nitrification reaction, and the continuous nitrification method of microchannel reactor is more suitable for large-scale production.
Conclusion
For the dangerous process of nitrification, the continuous flow reactor shows its significant advantages and achieves intrinsic safety. Its efficient reaction times, consistent compound quality, low-risk safety, highly automated control, and space-saving equipment design have revolutionized chemical production
-
Microchannel Reactor
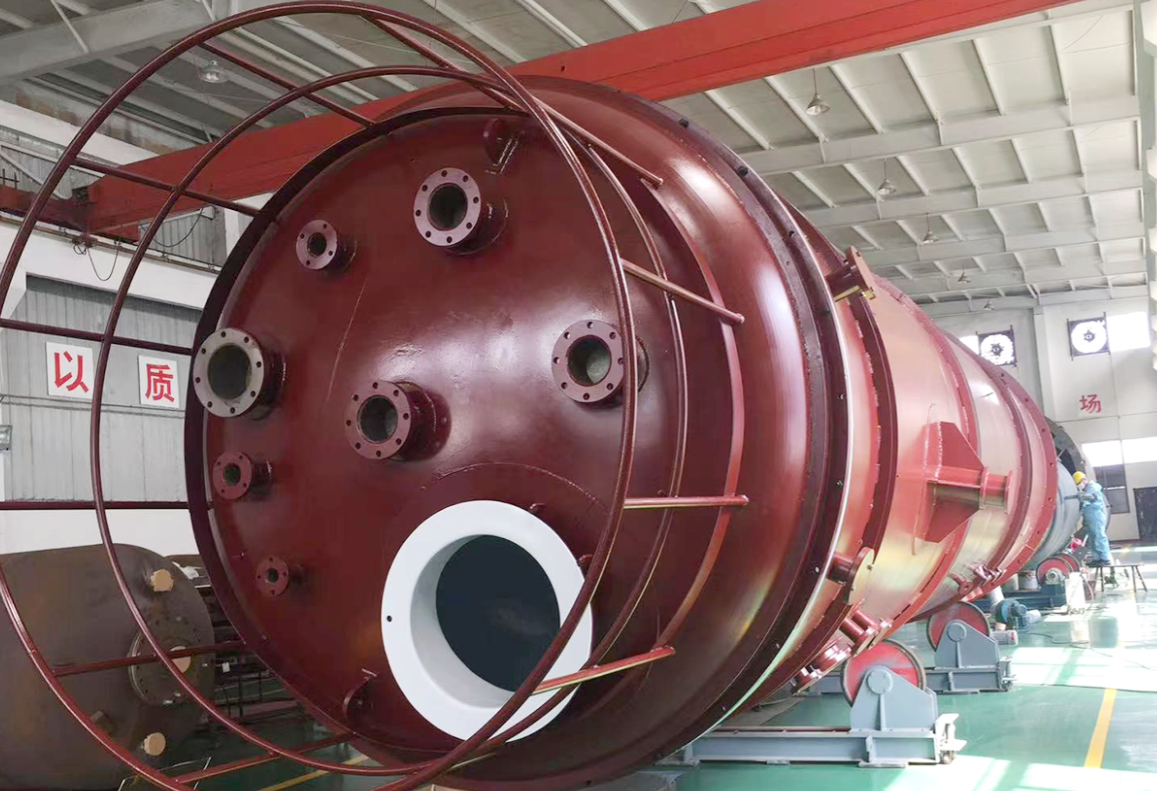
The essence of a chemical reaction is the process of breaking old chemical bonds and forming new ones, and the reactor is the carier of thechemical reaction, providina the necessary space and conditions for the reaction, As long as there is a place for reaction. the reactor is indispensable. The current reactors are even more diverse. They are widely used in the fields of medicine and food, chemicals, rubber, pesticides, dyes, etcThey are vessels used to complete processes such as vulcanization,nitration, hydrogenation, akylation, polymerization, and condensation. We specialize in the production of chemical reaction series containers. it hasreactors that can be adapted to varous reactions, and provides eauioment and technical services to university laboratonies, corporate R&D andchemical plants.
价格: 0.00 -
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE-lined anti-corrosion) has a high degree of chemical stability, it can resist almost all commonly used strong corrosion, hydroxide chemicals, and also has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, so it is an ideal anti-corrosion material.
价格: 0.00
Related Products
News
-
 View Details ➜
View Details ➜Application of Continuous Flow Reactors in High-Risk Processes
According to the State Council's Work Safety Committee, high-risk chemical processes include nitrati
-
 View Details ➜
View Details ➜Significant Advantages of Microreactors Over Conventional Tank Reactors
Microreactors have significant advantages over conventional tank reactors. They can precisely contro

3153-3 Lvxiang Village, Jinshan District, Shanghai
No.1, Sanqiang Road, Rugao City, Jiangsu
Tel: +86 13651755429;+86 13916961821
Email: ys.zhu@ekaislot.com;zsy@ekaislot.com
Contact Now